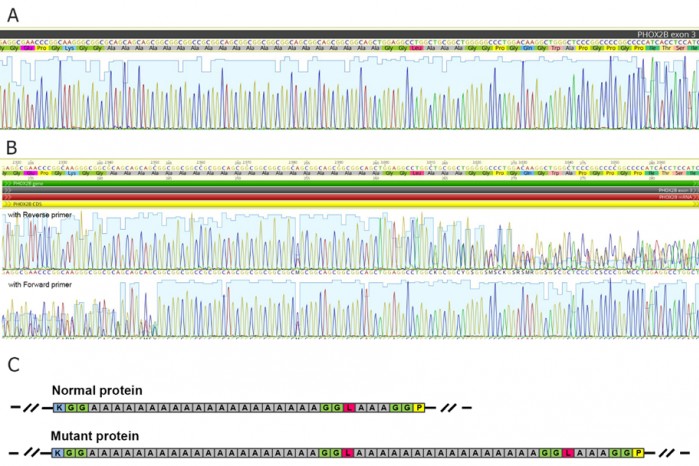
Specialists have described a case of central hypoventilation syndrome (CHS) with a mutation in the PHOX2B gene with expansion to 36 alanines interrupted by three other amino acids.
This type of mutation was described only in an experimental study by Trochet et al. (2005), who found normalized transactivation and DNA binding upon interruption of polyalanine expansion.
It is known that in 90% of CHS cases, a mutation in the PHOX2B gene leads to a duplication of the polyalanine repeat with the expansion to 24-33 amino acids, and the severity of phenotypic manifestations is directly proportional to the length of the polyalanine tract, requiring a round-the-clock ventilatory support with the largest number of repeats.
We have described for the first time a clinical case confirming the possible «protective» role of the inclusion of other amino acids in polyalanine expansion. Thus, a patient with the NM_003924.4: c.735_791dup mutation in the PHOX2B gene, despite expansion to 36 alanines, has a phenotype with moderate hypoventilation (only during sleep), as well as Hirschsprung disease, type 1, and cardiovascular anomalies. The new data obtained will allow a better understanding of the molecular genetic mechanisms of the disease and phenotype-genotype correlations for the timely initiation of patient-tailored therapy. The description of the clinical observation will be published in a top tier journal.
To learn more, please read the news of the WCRC for Personalized Medicine.
